Diabetes is a common ailment that affects seniors in the U.S. The condition may be medically diagnosed or may remain undiagnosed. When a diabetes diagnosis is made, it is vital that family members and caregivers help the elderly patient manage the condition.
The American Diabetes Association reports that 34.2 million Americans live with diabetes. The percentage of seniors aged 65 and older who suffer from diabetes is also high, at 26.8 percent, or 14.3 million individuals. These statistics include both diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes.
Seniors might have diabetes but not realize it. Symptoms of diabetes develop slowly, which makes it difficult to notice or detect right away. Older adults with the condition may attribute the symptoms to aging and dismiss the likelihood of disease. Consequently, the condition goes undiagnosed.
Diabetes is far from being a mild illness. In the U.S., the seventh leading cause of death is diabetes. In 2017 alone, 83,564 death certificates listed diabetes as an underlying cause of death. In the same year, 270,702 death certificates indicated that diabetes was a cause of death.
When left unmanaged, diabetes can also result in severe health problems. The disease adversely affects several systems in the body, including the heart, kidneys and eyes. A diabetic patient may experience a stroke or suffer from nerve damage; the latter can lead to amputation.
In type 2 diabetes, which commonly affects the elderly, a range of symptoms may develop. Hunger, thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision or unintentional weight loss may occur. Seniors diagnosed with diabetes also have a higher risk for cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
Although diabetes is a lifelong condition, seniors can manage the disease with help from family members and caregivers. Blood glucose levels can be successfully controlled with physical exercise and diet. Some seniors may be prescribed diabetes pills or receive insulin injections.
A diabetes management plan will be developed with the help of the senior’s healthcare team, which will include the senior’s physician, a diabetes educator, a dietician, and an exercise coach. Family members and caregivers should ensure the senior follows the healthcare plan.
1. Manage diabetes medications
The elderly individual’s doctor may prescribe one or more diabetes medications. For example, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, like Glyset, slow the digestion of sugars. Glynase and Diabeta are drugs that help the body produce insulin. Glucophage improves the body’s use of insulin.
When diabetes pills are prescribed, the senior’s caregiver is instrumental in ensuring the care recipient takes the right medications on schedule. Medication side effects, like low blood sugar, can occur. Caregivers will be attentive and responsive when side effects cause problems.
2. Plan nutritious meals
After a diabetes diagnosis, a dietician will help with meal planning. A healthy diet is one that that is low in sugars, including sugars in fruits, and trans- and saturated fats. Cholesterol should be limited to 200mg or less per day. Reduce sodium to no more than 2000mg per day.
One responsibility that professional caregivers routinely carry out is grocery shopping. Caregivers will shop for healthy foods suitable for a diabetic patient. Lean proteins, fresh vegetables, quinoa, beans, apples, and dairy products low in fat can be found on a caregiver’s shopping list.
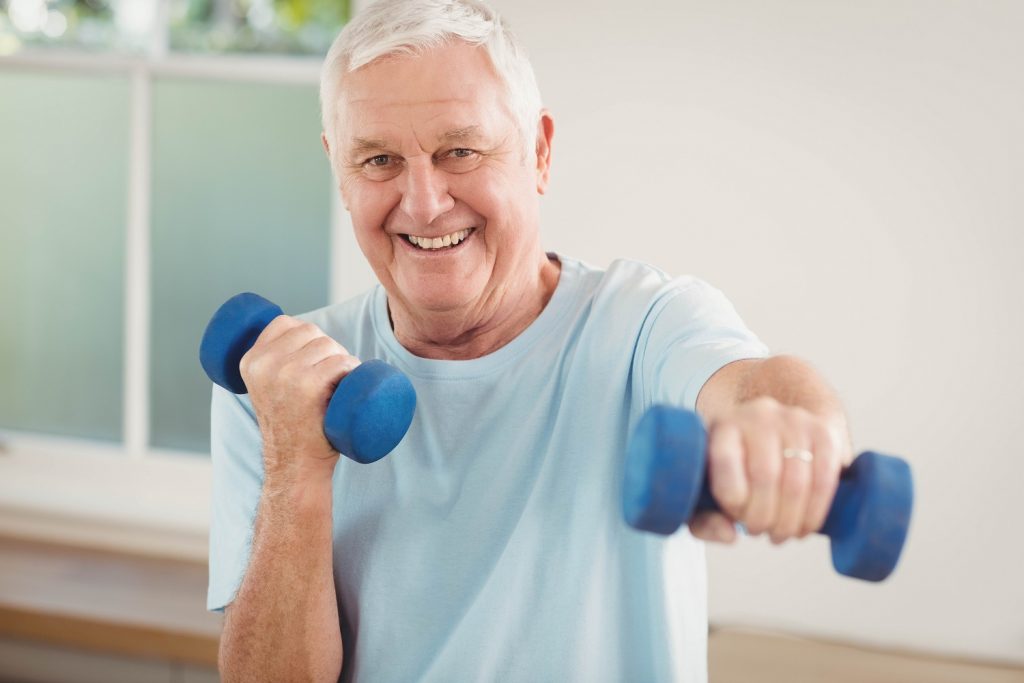
3. Encourage physical exercise
An exercise coach will recommend physical activities to the senior newly diagnosed with diabetes. Aerobic exercises are key to managing the disease. Seniors may participate in walking, swimming, or bicycling to control glucose levels, manage weight, and maintain physical strength.
Strength training is necessary to build muscles and manage glucose levels. Performing yoga, lifting free weights, and using resistance bands are examples of strength training exercises. While aerobic activity is recommended five days a week, strength training should be done twice a week.
Seniors who lack confidence in physical exercise will receive plenty of support from caregivers. These professionals are trained to provide mobility assistance. Older adults can expect caregivers to accompany them on walks or provide safe transport to senior exercise classes.
4. Monitor daily health
In addition to eating a nutrient-rich diet and getting regular exercise, older diabetic patients must routinely check their blood glucose levels. Low blood sugar levels are 70mg or lower. Normal blood sugar levels, before consuming a meal, range from 70mg to 130mg.
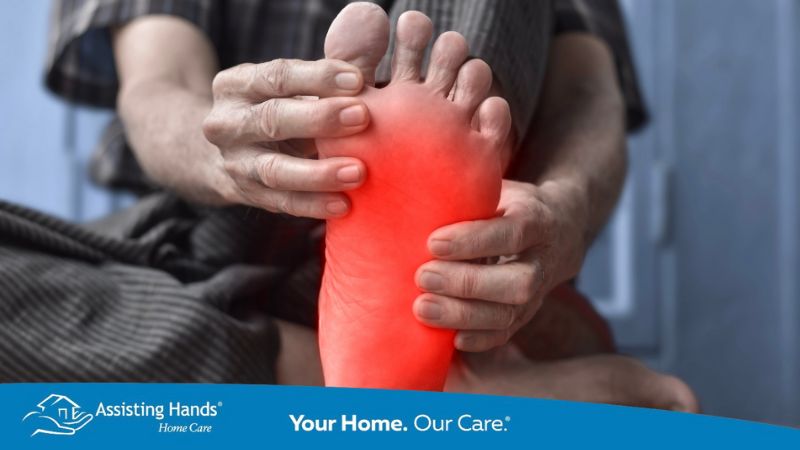
Seniors who are unable to check their blood glucose levels rely on caregivers for help. These professionals also examine seniors’ feet for signs of infection. Gum disease is common in diabetic patients. Caregivers ensure dental health by transporting care recipients to dental appointments.
Diabetes management in the elderly varies significantly and is influenced by variable factors, such as social support, cognitive and physical functioning, and living situations. While high-functioning seniors can independently perform self-care, those with impairments will need additional help at home.

Assisting Hands Home Care is a critical resource for seniors living with diabetes. Professional caregivers from our reputable home care agency are trained to provide a wide range of non-medical services that support the emotional and physical well-being of seniors in our care.
Older adults with any level of cognitive or physical impairment rely on our caregiving teams for daily in-home support. Diabetic patients receive timely medication reminders, are transported to doctors’ appointments for check-ups, get help with mobility, and eat healthy meals prepared by our caregivers.
Professional caregivers from Assisting Hands Home Care also meet the care needs of seniors living with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, as well as hospice patients. We provide reliable respite care to families who are focused on caring for their elderly loved ones at home.
Whether the senior in your life would benefit from quality memory care, compassionate respite care, post-operative care, or any other type of non-medical home care, choose Assisting Hands Home Care. We offer comprehensive senior care services that are flexible and meet various scheduling needs.
Assisting Hands Home Care is privileged to support the elderly living in Joliet, Oswego, Plainfield, Romeoville, Yorkville, Bolingbrook, and surrounding areas in Will and Kendall Counties. Schedule an in-home consultation to start your elderly loved one on a path toward improved well-being and a higher quality of life.